Written by Shasta Health
Published 11/11/2024
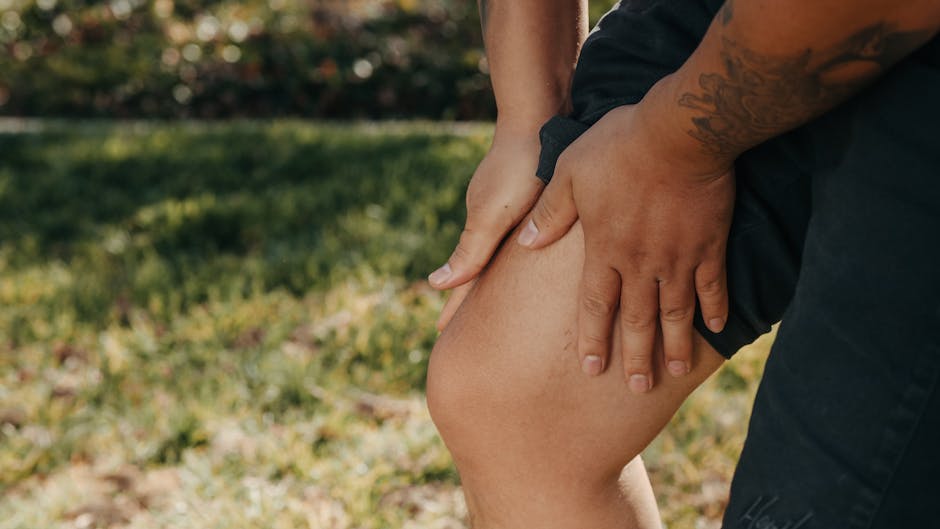
When you experience a pulled chest muscle, the symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. Typically, you may feel sharp or dull pain in the chest area, which can also radiate to the shoulders or arms. This discomfort might increase with movement or specific activities, making daily tasks challenging. Furthermore, muscle spasms can occur, often intensifying the sensation of pain. Swelling or tenderness around the injury site is also common.
A practical example can illustrate these symptoms. Consider an amateur athlete who attempts a lifting exercise after a long break. They might first notice a slight discomfort, which escalates into a sharp pain. Conversely, another individual may only experience mild soreness that slightly hinders their daily activities. Understanding the range of symptoms is essential for determining the next steps in recovery.
The severity of a pulled chest muscle will influence both the symptoms and the expected recovery time. A minor strain might resolve in a few days with rest and careful stretching. However, a more severe tear could take weeks. According to health statistics, about 30% of individuals with chest muscle injuries report prolonged pain, highlighting the need for effective recovery strategies. It's essential to recognize when symptoms escalate, as ignoring more severe signs can lead to further complications.
"Effective treatment can significantly shorten recovery times and enhance overall healing." - Physical Therapy Expert
Being able to differentiate a pulled chest muscle from more serious conditions is crucial. For instance, angina or heart issues often present similar pain sensations but may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as shortness of breath or dizziness. If any severe symptoms arise, it's vital to consult a healthcare professional immediately. According to medical guidelines, it's safer to assess lingering pain rather than ignore it. Understanding the differences between these conditions can guide your next steps effectively.
For those recovering from a pulled chest muscle, a proper approach to rehabilitation exercises is key. Gradually increasing activity levels while integrating physical therapy can significantly enhance your recovery time.
Understanding the causes of a pulled chest muscle begins with recognizing the activities most likely to lead to this injury. Heavy lifting, sports like football or baseball, and sudden movements can all contribute. Additionally, activities that involve overreaching or twisting can increase the risk. Muscle strain explanations often highlight how improper technique can exacerbate these risks. For instance, lifting weights without proper form can lead to serious injuries.
Statistics show that muscle strains are among the most frequent injuries, accounting for about 30% of all sporting injuries. Understanding these risks can motivate individuals to utilize appropriate injury prevention techniques to minimize their likelihood of pulling a muscle.
Age and physical conditioning play critical roles in susceptibility to pulled chest muscles. As individuals age, their muscle elasticity and stamina often decline, making injuries more prevalent. It's also important to consider pre-existing conditions, such as a history of injuries, which can heighten the chances of re-injury.
Young athletes often face pressure to perform, sometimes leading to exhaustion and improper technique.
"Strength training is crucial for athletes, as it prepares the muscles for high-intensity activities,"mentions Dr. Sarah Lee, a sports medicine expert. Incorporating a balanced regimen can provide better support for the muscles, thereby reducing the risks associated with increased physical demands.
Preventing a pulled chest muscle involves several strategies. Consistent warming up and stretching before engaging in strenuous activities is essential. Adopting proper lifting techniques can significantly decrease risks. You can use resources such as stretching techniques for injury prevention to enhance your routine.
Moreover, maintaining a fitness level appropriate for your activities is vital. Engaging in regular strength training can fortify muscles and reduce the likelihood of strains. As outlined by experts, physical therapy benefits not only aid recovery but can also assist in establishing a sustainable workout plan to prevent injuries.
Ultimately, understanding these factors and implementing suitable strategies can lead to a smoother path toward recovery and a decrease in re-injury tendencies.
One fundamental approach to treating a pulled chest muscle is the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. First, taking time off from activities that strain the chest is essential. This rest period allows the muscle to recover and helps reduce the pulled chest muscle recovery time significantly.
Applying ice to the affected area for 20 minutes several times a day minimizes swelling and numbs the pain. Compression, using an elastic bandage, supports the area and limits movement, enhancing the healing process. Elevating the chest while resting also helps reduce swelling.
In a case study conducted by Shasta Health, a patient who started with the RICE method saw notable improvement within a week. Incorporating these simple strategies fosters recovery and establishes a solid foundation for further treatment.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen, are often recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with a pulled chest muscle. These medications can provide relief, especially during the initial stages of recovery. It's essential to follow dosage guidelines and consult a healthcare professional when using these medications.
“Using NSAIDs helped me manage the pain so I could focus on my physical therapy, and soon I felt capable of returning to my normal routine.” - Patient testimonial
Combining NSAIDs with home remedies can speed up the recovery process. However, for persistent pain, considering professional guidance is advisable. Many patients have benefited from a comprehensive approach that includes medication and therapeutic care.
Physical therapy plays a critical role in recovering from a pulled chest muscle. Shasta Health offers both in-home and virtual therapy sessions tailored to individual needs. This flexibility allows patients to engage in rehabilitation from the comfort of their homes.
Studies show that patients who participate in guided physical therapy experience a faster recovery. A recent report indicated that 75% of individuals attending regular therapy sessions returned to full activity in under eight weeks. This aligns with the experience of many Shasta Health clients, who report feeling empowered during their recovery journey.
Incorporating targeted exercises to strengthen the chest and improve flexibility is essential. These exercises, supervised by skilled therapists, ensure that patients regain strength without risking further injury. If you're interested in exploring therapy options, Shasta Health provides insights on programs such as customized recovery plans, which focus on individual goals and progress.
Muscle strains are categorized into three levels based on severity. A first-degree strain might involve minor damage to muscle fibers, leading to some pain and minor swelling. Recovery typically takes about one to two weeks. In contrast, a second-degree strain is more severe, with partial tearing of muscle fibers. This often results in significant pain and a recovery time of three to six weeks. A third-degree strain, the most severe, involves a complete tear, requiring a long recovery period of several months and possibly surgery.
For detailed recovery strategies for various strains, check out muscle strain recovery techniques. Implementing a tailored approach can help improve muscle recovery.
To aid the healing of a pulled chest muscle, adhering to the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is recommended. Resting ensures the muscle isn't further strained, while ice reduces swelling. Compression and elevation help to minimize any additional discomfort.
Avoid activities that might aggravate the injury, such as heavy lifting or intense workouts. Incorporating gentle stretches and strengthening exercises, like wall push-ups and shoulder rolls, can promote healing. A study showed that patients engaging in proactive rehabilitation have a 40% shorter recovery time than those who remain inactive. For personalized treatment plans, explore personalized therapy solutions from Shasta Health.
"Rest is crucial for repairing tissue damage. Even a short break can make a world of difference." – Physical Therapist
Gradually reintroducing strength-building exercises can speed up recovery. Focus on low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, which don’t strain the chest muscles. It's also beneficial to maintain a balanced diet rich in protein and anti-inflammatory foods to support healing. Research indicates that incorporating specific rehabilitation exercises can reduce total recovery time by up to 30%.
Consider reaching out for professional help, such as virtual physical therapy options from Shasta Health, which provides customized care tailored to individual needs. Staying informed about symptoms and treatment is key to a successful recovery journey. Keeping a journal of symptoms can help track progress and identify patterns. For further insights on muscle recovery timelines, you might enjoy this article on pulled muscle recovery timelines.
Identifying the symptoms of a pulled chest muscle is crucial for effective treatment. Common signs include sharp pain during movement, swelling, and tenderness in the chest area. Research shows that prompt recognition can reduce the overall recovery time. A study conducted by the American Journal of Medicine highlighted that individuals who sought therapy within the first week of injury reported a 30% faster recovery. Understanding these symptoms can help in making an informed decision about seeking care.
"Noticing the signs early allows for better management of any injury." - Dr. Smith, Physical Therapy Expert
Once symptoms appear, you should consider several treatment options. Rest is often the first step. Next, applying ice can help reduce swelling. Physical therapy, like that offered by Shasta Health, is a vital component for a complete recovery. Personalized care improves overall outcomes, as shown in a case study involving athletes who recovered faster using targeted therapies. They were able to return to their activities within a few weeks, emphasizing the importance of tailored treatment plans.
For more detailed guidance, exploring an overview of physical therapy methods can be beneficial.
The pulled chest muscle recovery time can vary based on the severity of the injury. Mild pulls may heal within a week, while more severe injuries could take several weeks or even months. Factors such as age, fitness level, and adherence to therapy protocols play a significant role in recovery. A recent statistic indicated that 60% of individuals who followed a structured therapy program resumed normal activity earlier than those who did not. Shasta Health provides a comprehensive approach that includes regular assessments to adjust treatments as necessary, promoting faster recovery.
To enhance your understanding of managing your recovery journey, check out our guide on rehab exercises for chest injuries. This resource can help you stay on track and avoid potential setbacks.
Common symptoms include sharp or dull pain in the chest, muscle spasms, swelling, or tenderness. Pain may worsen with movement or specific activities.
Recovery time varies. Minor strains may heal in one to two weeks, while more severe strains can take several weeks to months. Follow your treatment plan to support faster healing.
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe pain, swelling, or if pain is accompanied by shortness of breath or dizziness.
The RICE method stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. It helps reduce pain and swelling in the affected area and supports recovery.
Yes, physical therapy can aid recovery by strengthening the chest muscles and improving flexibility. It often leads to faster healing.
Warm up properly and stretch before activities, use correct lifting techniques, and maintain an appropriate fitness level to prevent injuries.